Affordable Housing in Modern-Day America: Its Importance and Economic Drivers
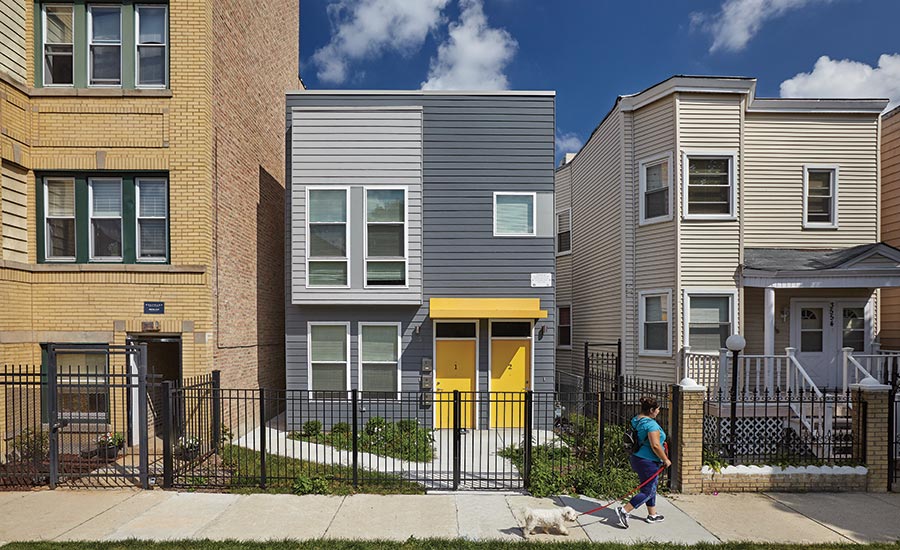

Affordable housing has evolved from a mere policy issue to a linchpin that holds together economic stability, social equality, and community health. At a time when housing costs are skyrocketing in numerous cities across the United States, the subject of affordable housing has become not just a talking point but an urgent call for action.
This piece aims to shed light on the importance of affordable housing for the overall fabric of society and discuss the key economic drivers that shape its landscape.
Importance of Affordable Housing
The significance of affordable housing extends far beyond mere bricks and mortar; it serves as a cornerstone for broader societal well-being. Factors such as social stability, health outcomes, economic mobility, and overall quality of life must be considered to fully appreciate its impact.
Consider the following key areas to grasp the multi-faceted impact of affordable housing:
Social Stability
Affordable housing plays a critical role in fostering social stability. In communities where housing is affordable, residents are less likely to face eviction or homelessness, thus maintaining a sense of community cohesion. According to a study by the Joint Center for Housing Studies at Harvard, people spending more than 30% of their income on housing are at a greater risk of financial instability.
Health Outcomes
Living conditions directly impact health outcomes. Substandard housing often exposes residents to health hazards like mold, poor water quality, and inadequate heating, leading to chronic illnesses. A Robert Wood Johnson Foundation report outlines how affordable, quality housing is an essential physical and mental health determinant.
Economic Mobility
Housing stability is a cornerstone for economic mobility. People living close to job markets because of affordable housing have better employment opportunities, can maintain jobs, and climb the economic ladder. A study found that children who moved to low-poverty neighborhoods had higher incomes as adults than those who stayed in high-poverty areas.
Quality of Life
Affordable housing significantly improves the quality of life for families by allowing them to allocate funds to education, healthcare, and other necessities that elevate their socio-economic conditions. Studies have shown that affordable housing near quality schools significantly impacts educational outcomes for children.
Key Economic Factors Driving Affordable Housing
Formulating more effective strategies for facilitating housing affordability requires a comprehensive grasp of various economic influences, including labor market shifts, rising costs in diverse sectors, and regulatory obstacles. This issue doesn't exist in isolation but is deeply interconnected with broader economic dynamics.
For a nuanced understanding of how affordable housing is influenced, it's essential to examine these pivotal economic drivers:
Labor Market Shifts
The decoupling of wages from the cost of living is a significant challenge. Many working in service industry jobs cannot afford to live in the cities where they work, leading to unsustainable commuting or homelessness.
Rising Costs
Inflationary pressures in various sectors, including healthcare and education, make it even more difficult for families to allocate funds for housing. This perpetuates a cycle where the lack of affordable housing feeds into broader economic instability. A study by the National Association of Home Builders showed that regulatory costs account for about 23.8% of the price of a new single-family home.
Supply and Demand
A housing supply that does not meet the demand, especially for low- and middle-income families, naturally drives up the costs. High demand for limited urban land and the slow pace of construction contribute to this imbalance.
Zoning Regulations and Government Policies
Stringent zoning regulations can restrict the types of homes that can be built, thus limiting the supply of affordable housing. On the positive side, government programs like the Low-Income Housing Tax Credit (LIHTC) aim to incentivize the construction of affordable units.
Land Availability
In densely populated areas, land availability becomes a constraint for building affordable housing. Alternative solutions like vertical housing need to be explored and incentivized.
Community, Capital, and Care
Affordable housing is not just a social welfare policy but an economic and healthcare imperative. It ties into broader social stability issues, health outcomes, and economic mobility, enriching the overall quality of life. However, achieving this is fraught with challenges like shifting labor markets, rising costs in other sectors, supply-demand imbalance, and regulatory hindrances. Policy changes that address these economic drivers can create a more balanced and socially equitable landscape for affordable housing in modern-day America.