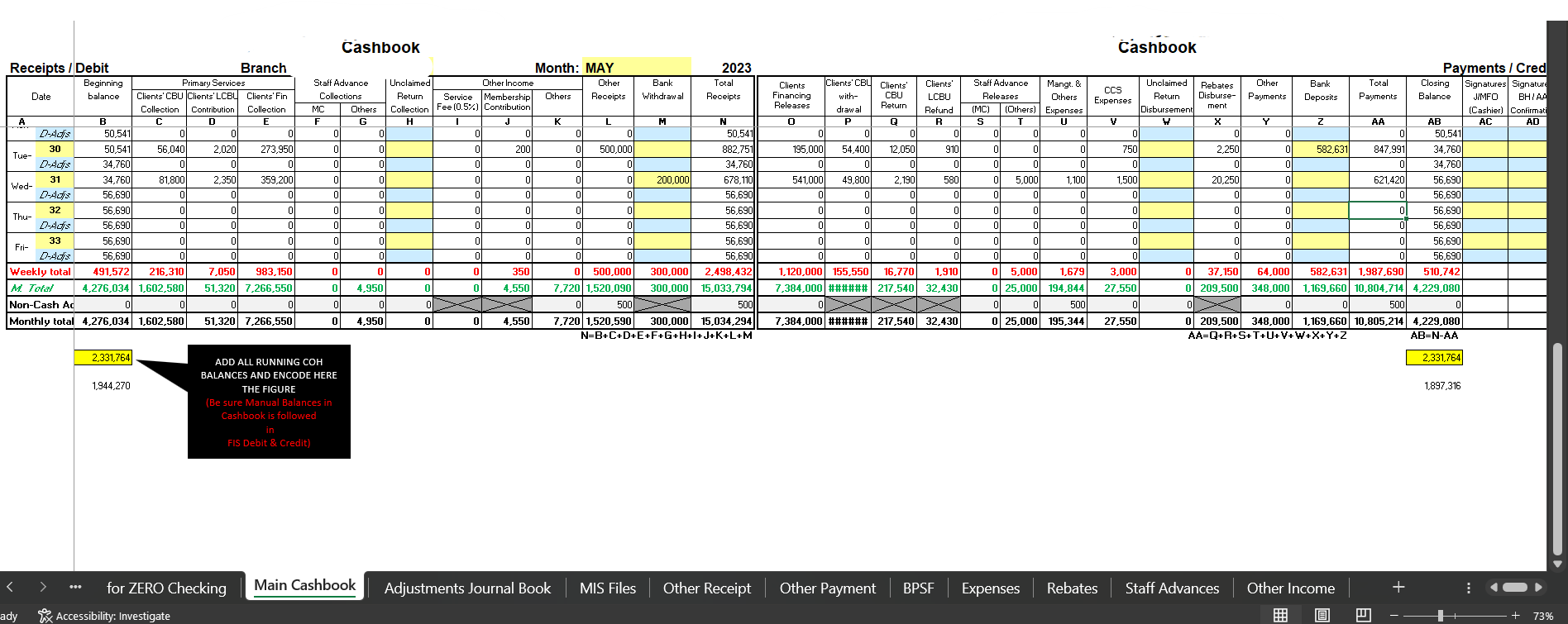
Bookkeeping
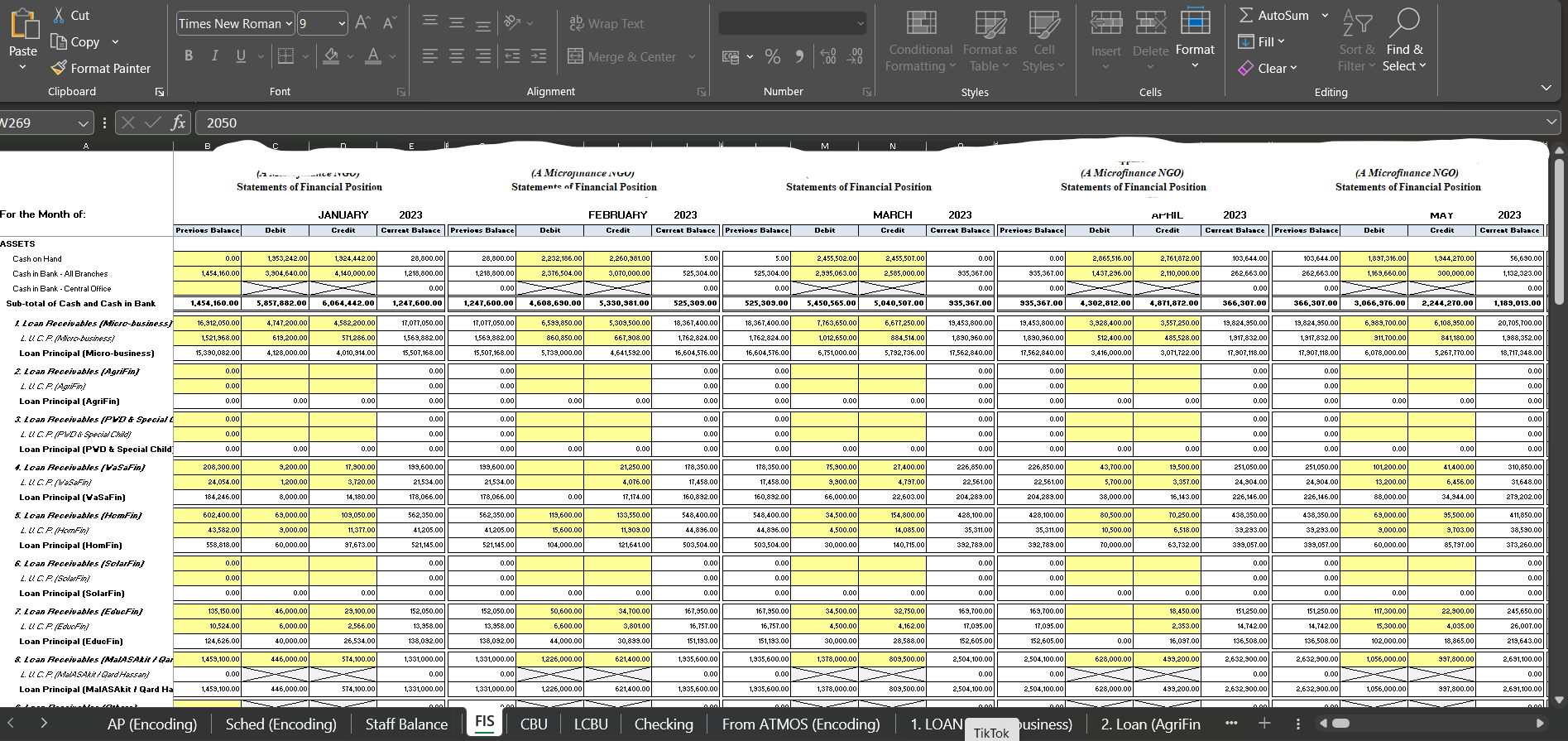
MIS stands for "Management Information System." It is a computer-based system that collects, processes, stores, and disseminates information to support decision-making, coordination, control, analysis, and visualization of an organization's activities. MIS is designed to provide managers and other stakeholders with timely and relevant information to help them make informed decisions and manage the organization effectively.
The main objectives of an MIS include:
Data Collection: Gathering data from various sources within the organization and external sources as required.
Data Processing: Organizing, aggregating, and processing the collected data into meaningful information.
Data Storage: Storing the processed data in databases or other suitable formats for easy retrieval and analysis.
Information Dissemination: Distributing the information to relevant individuals or departments in a timely manner.
Decision Support: Providing the necessary information and tools to support decision-making processes at various levels of management.
Planning and Control: Assisting in the planning and control of organizational activities by providing real-time data and performance metrics.
Performance Evaluation: Evaluating the performance of various departments or processes through data analysis.
MIS plays a vital role in modern organizations, helping them streamline operations, improve efficiency, reduce costs, and gain a competitive advantage in the marketplace. It involves the use of computer systems, software applications, databases, and communication networks to manage and process data effectively.