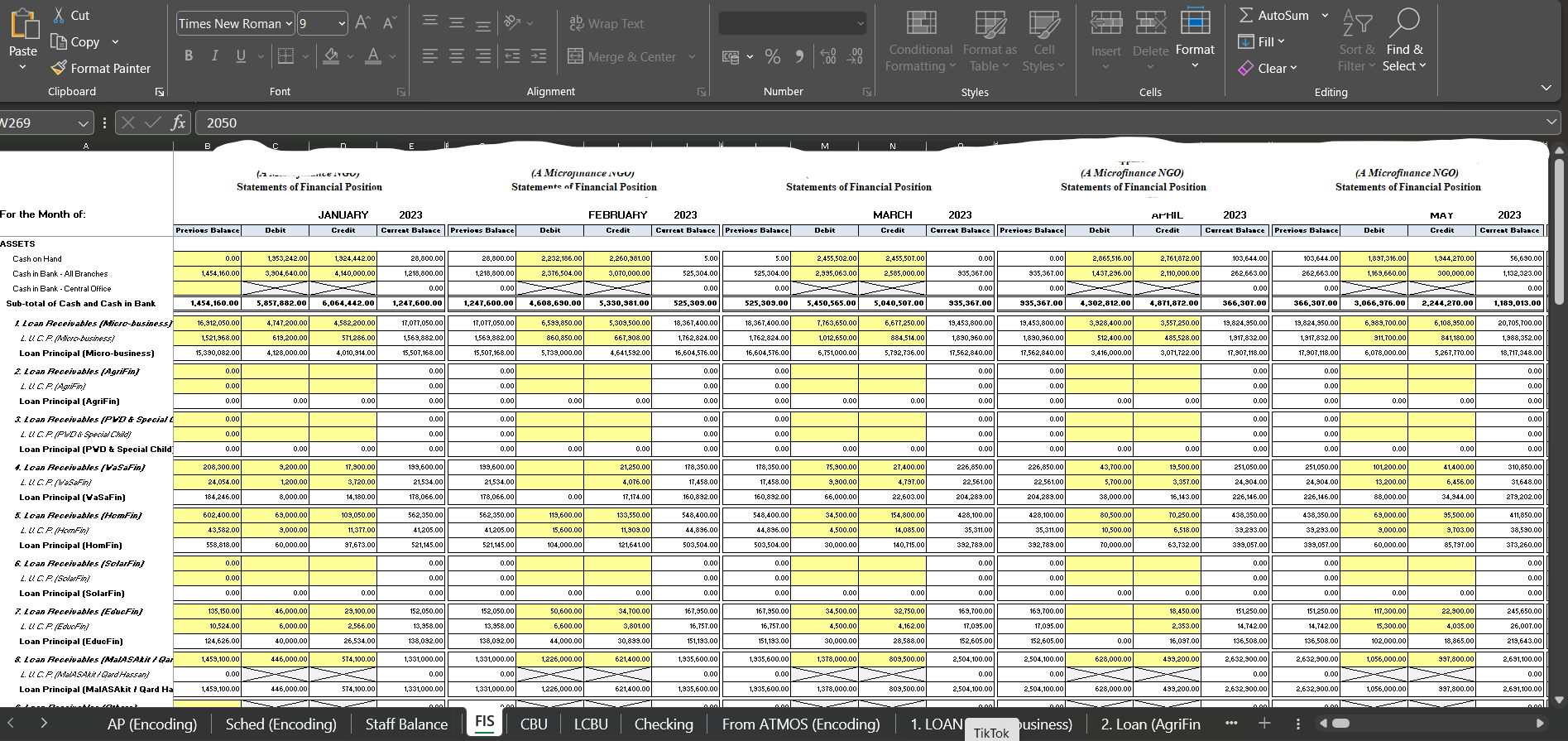
Bookkeeping
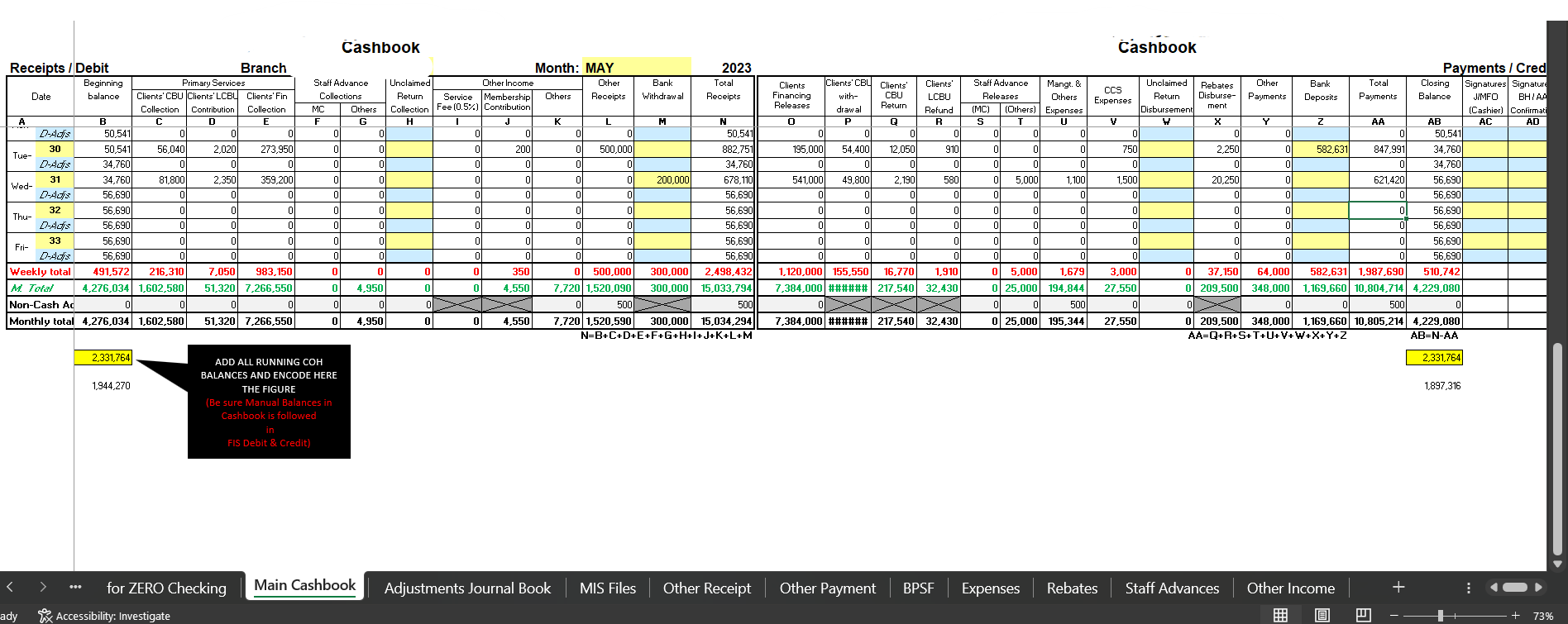
A cashbook is a financial record used to track cash transactions in a business or personal account. The content typically included in a cashbook may vary depending on the level of detail required, but the basic elements typically consist of:
Date: The date of each cash transaction is recorded to maintain chronological order.
Description: A brief description of the transaction, such as "sales revenue," "purchases," "rent," "utilities," "salaries," etc.
Debit: The amount of money received or expended in each transaction is entered on the debit side of the cashbook.
Credit: The amount of money paid out or received in each transaction is entered on the credit side of the cashbook.
Running Balance: The cashbook should include a running balance, which is the result of the mathematical calculation of the debit and credit amounts. This allows the account balance to be updated after each transaction.
Source/Reference: Any additional information or reference numbers related to the transaction, like invoice numbers, payment references, or customer names.
Bank/Cash: Indication of whether the transaction relates to cash in hand or bank transactions.
Bank Statement Reconciliation: If the cashbook is used to reconcile with bank statements, there might be additional columns or notes to match transactions with the bank records.
Closing Balance: The final balance at the end of a specific period, such as a day, week, or month.
Notes/Comments: Optional space for any additional notes or comments regarding specific transactions or events.
The cashbook plays a crucial role in maintaining accurate financial records, tracking cash flow, and helping with financial analysis and decision-making. It can be recorded manually in a physical ledger or electronically using accounting software.